top of page

Geology
Scroll down for review reading materials, lesson videos and diagrams.
Minerals

minerals
To be considered a mineral, the substance in question must meet the following criteria:
• Naturally occurring
• Solid
• Inorganic
• Definite chemical composition
• Definite crystalline structure

How do we identify minerals?
COLOR
Most visible characteristic, but least reliable because many minerals share the same color and many minerals exist in different colors.


STREAK
The color of the mineral in powdered form (use a “streak plate”). Very reliable tool for identifying samples. Note: the color of the powdered form is often different from the color of the solid form.
FRACTURE/ CLEAVAGE
Cleavage is the tendency of a mineral to split along one or more smooth, flat surfaces. If a mineral does not display cleavage, it is said to have fracture, which means it breaks unevenly.

HARDNESS
The mineral’s resistance to being scratched. Minerals are compared to the ten minerals
on the “Moh’s Scale of Hardness”. Minerals are often compared to glass (hardness: 5.5)

LUSTER
Either metallic (shiny, like a polished metal) or nonmetallic (dull, with no shine). Types of nonmetallic luster include glossy, pearly, greasy, etc.


OTHER CHARACTERISTICS
that can be tested include: magnetism, reaction with chemicals, taste, specific gravity, crystal form, fluorescence, optics.

Calcite reaction to acid
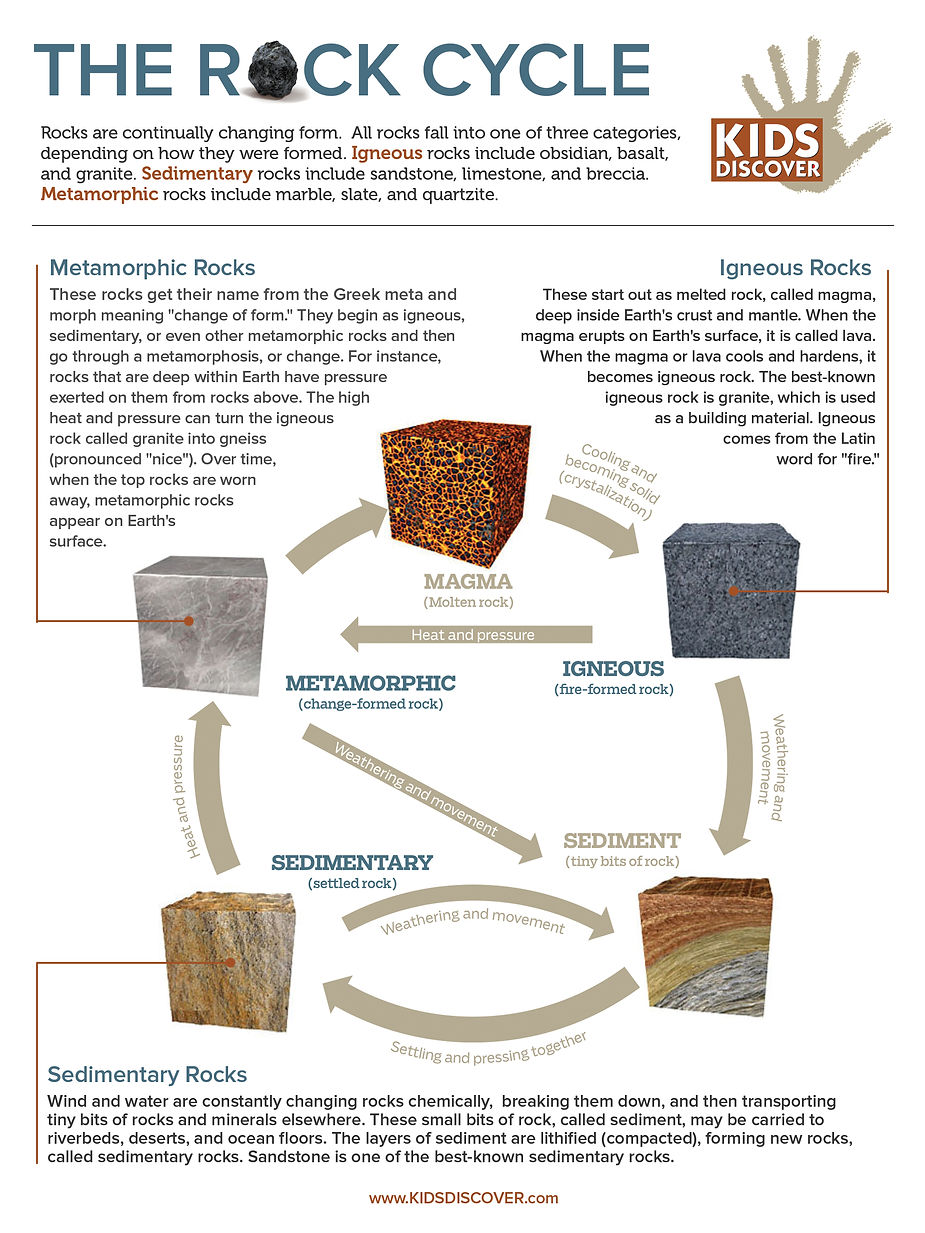
Rocks

rocks
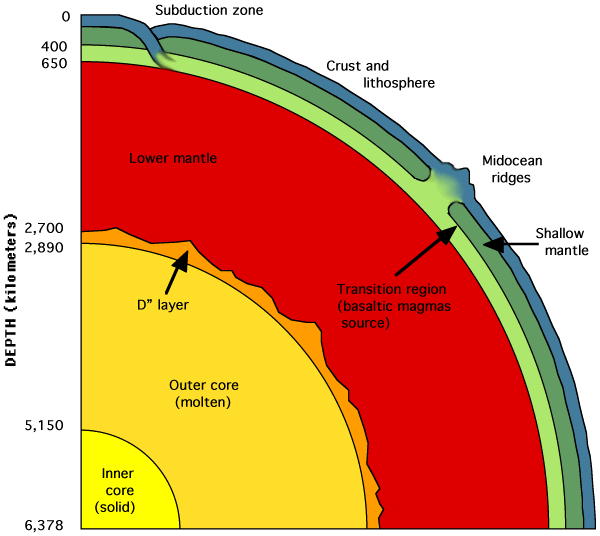
Earth Interior

Earths Interior
bottom of page
