
DYNAMIC CRUST
Earth may be considered a huge machine driven by two engines, one internal and one external. These heat engines
convert heat energy into mechanical energy. Earth’s internal heat engine is powered by heat from the decay of
radioactive materials and residual heat from Earth’s formation. Differences in density resulting from heat flow within
Earth’s interior caused the changes explained by the theory of plate tectonics: movement of the lithospheric plates;
earthquakes; volcanoes; and the deformation and metamorphism of rocks during the formation of young mountains.

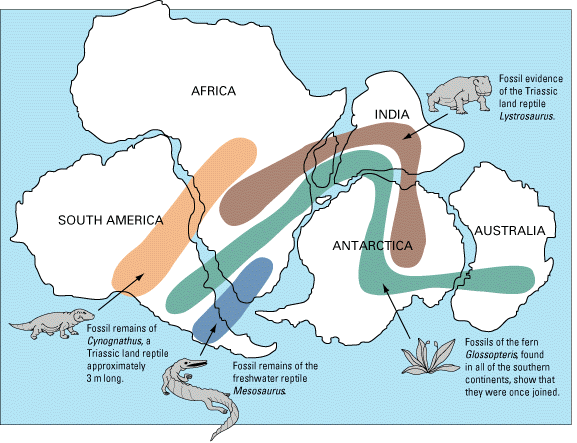
CONTINENTAL DRIFT



CONTINENTAL DRIFT ANIMATION

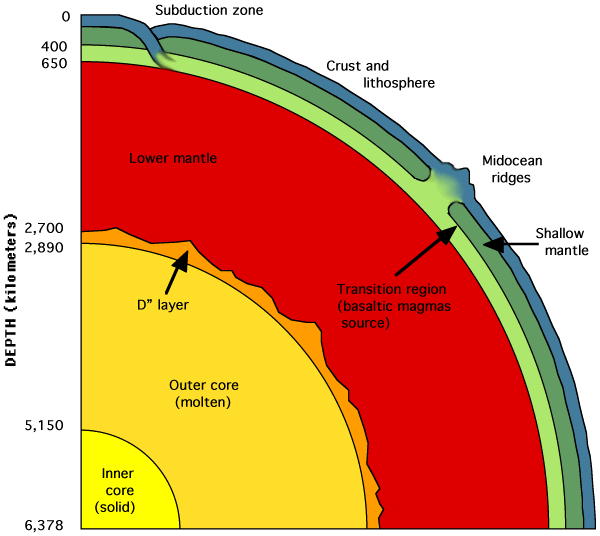
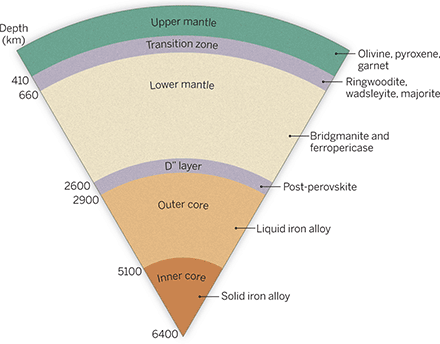
EARTH INTERIOR
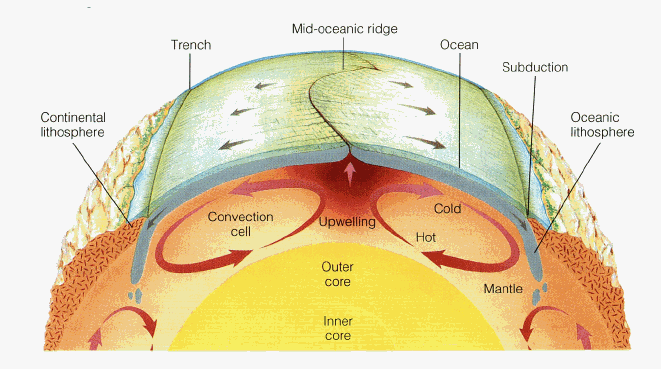
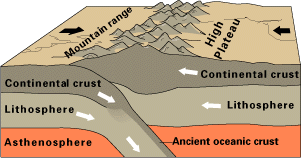
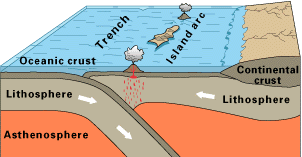
PLATE TECTONICS

PLATE BOUNDARIES
DIVERGENT
CONVERGENT

TRANSFORM AND HOT-SPOTS

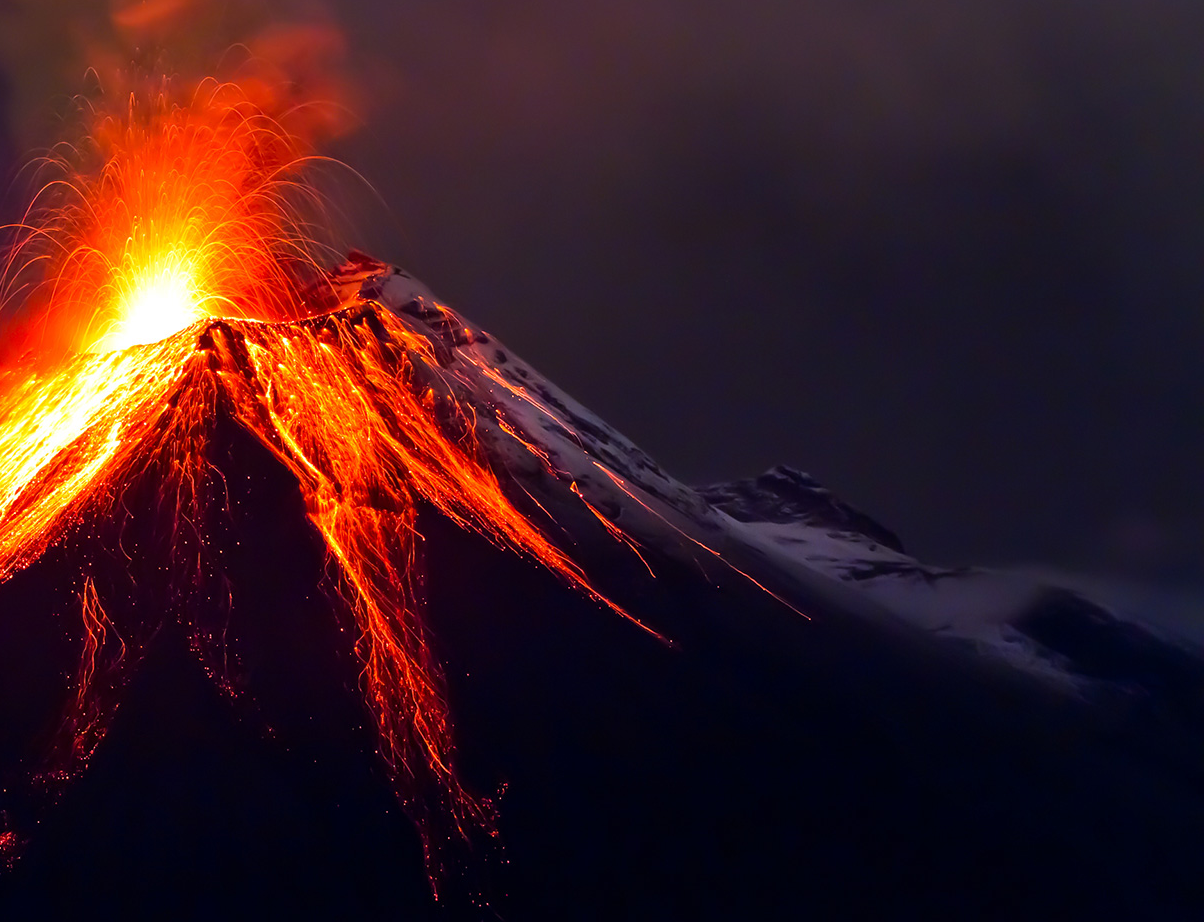
VOLCANOES
Most of the volcanic activity on Earth occurs along plate boundaries, in particular along diverging and converging boundaries. However, hot spot volcanism may occur far from plate boundaries.
Central volcanoes discharge lava or pyroclastic materials from a central vent. There are three types of central volcanoes: stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes and cinder volcanoes.
During a fissure eruption, lava is flowing out of a several tens of kilometers long crack In the Earth's surface.
TYPES OF VOLCANOES


FOOTAGE OF CALBUCO ERUPTION
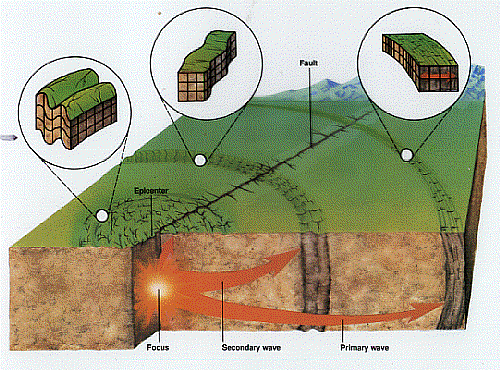
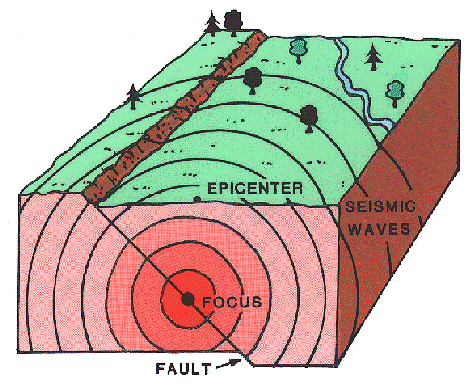
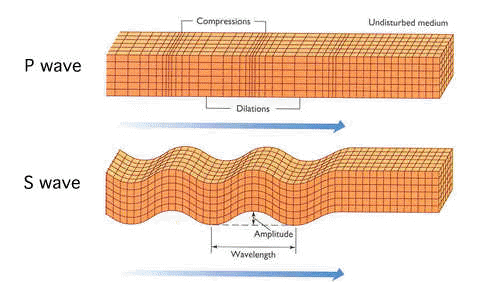
EARTHQUAKES
NOTE: The following video lessons will seem redundant at times, however it is important to remember that Part D of the regents has a station on finding epicenters.
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
CALCULATING DISTANCE TO EPICENTER
TRIANGULATION OF EPICENTERS
DETERMINING RICHTER MAGNITUDE
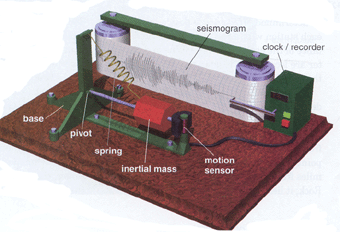
SEISMOGRAM ANALYSIS
3d Animation of Tsunami Generation
INTERACTIVE LESSONS
NOTE: These interactive lessons cover the material at a much more advanced level. Use them to help clarify key topics discussed in class.
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |